No Products in the Cart
Last Updated December 20, 2024
Do you ever feel like you're trapped in a cycle of tossing and turning at night, unable to catch a good night's sleep? And then, the next day, you're battling through grogginess and fatigue, struggling to keep your eyes open and stay focused. It's a frustrating and exhausting experience that many of us go through. But guess what? You're not alone. The good news is that there's a simple yet powerful solution that can help break this cycle: the sleep calculator.
In this blog post, we'll cover everything you need to know about sleep calculators, from how they work to the benefits they provide. Get ready to kiss those sleepless nights goodbye and wake up feeling energized every morning!
Key Takeaways:
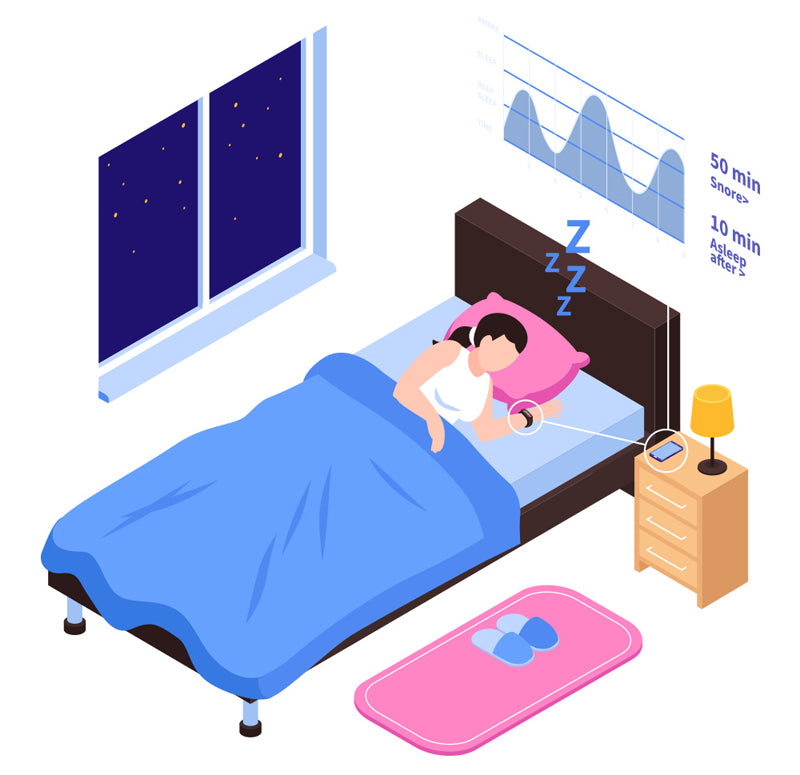

So, what exactly is a sleep calculator, and how does it work? At its core, a sleep calculator is a digital tool or application that assists individuals in optimizing their bedtime and wake-up time according to their specific sleep requirements and preferences. It functions by taking into account various factors, such as sleep cycles, recommended sleep duration, and personal lifestyle considerations, to generate an ideal sleep schedule.

Here's how a typical sleep cycle calculator works:
Feeling overwhelmed with all this information? Let us help you understand how a sleep cycle calculator works in a simpler way.
First, you need to know:
Let's say you were in bed for 7 hours (420 minutes), took 15 minutes to fall asleep, and spent another 15 minutes awake during the night.
To calculate your sleep efficiency:
This gives you the actual time you spent sleeping (390 minutes, or 6 hours and 30 minutes).
Finally, divide the actual time you spent sleeping (390 minutes) by the total time you were in bed (420 minutes) and multiply by 100 to get a percentage. In this case, it's 390/420 * 100 = 92.8%.
In sleep science, a sleep efficiency of 85% or higher is considered healthy, and aiming for around 90% is very good. If your score is lower, don't worry. By paying more attention to your sleep habits and possibly adjusting your bedtime, you can improve your sleep efficiency over time.

While there are some general rules about how much sleep people need, it can vary from person to person. This depends on things like your lifestyle, any health issues you might have, and even your genes. According to the National Sleep Foundation (NSF), different age groups should aim for the following amounts of sleep within a 24-hour period:
Now that you understand how sleep calculators can help you plan your sleep routine according to your needs, let us tell you why getting good sleep is so important. The truth is that sleep is essential for your overall health and well-being. It plays a big role in how your body works, how you think, and how you feel. Here's why catching those Z's is more important than you might think:
1. Restoration and Healing

While we're asleep, our bodies are busy repairing tissues, synthesizing proteins, and releasing essential hormones. This restorative process helps maintain optimal physical health and supports the immune system.
2. Brain Function and Cognitive Performance
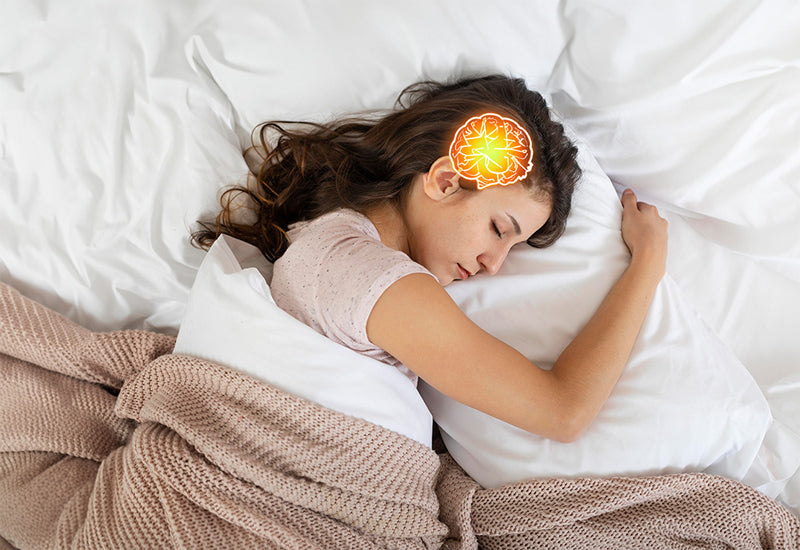

Sleep aids in the consolidation of memories, the processing of information, and the elimination of toxins built up throughout the day in your brain. This, in turn, enhances learning, concentration, problem-solving abilities, and overall cognitive function.
3. Emotional Well-being

Ever notice how cranky you feel after a sleepless night? That's because poor sleep can significantly impact our mood and emotional regulation. Sleep experts say that adequate rest is essential for maintaining a positive outlook, managing stress, and reducing the risk of mood disorders like depression and anxiety.
4. Physical Health

Chronic sleep deprivation has been closely associated with a host of serious health conditions, including obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension. By prioritizing sleep, we can lower our risk of these ailments and improve our overall quality of life.
5. Enhanced Performance and Productivity

Whether you're an athlete, a student, or a professional, getting enough sleep directly impacts your performance and productivity. Well-rested individuals are more alert, focused, and efficient, leading to better outcomes in both personal and professional endeavors.
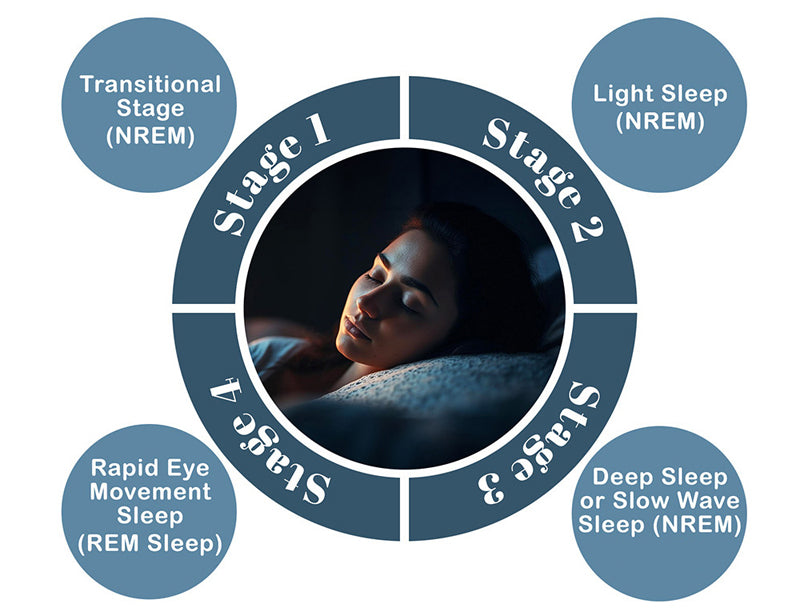
There are four distinct sleep stages: one characterized by rapid eye movement (REM) and the remaining three grouped under non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. These stages are identified through the analysis of specific brain activity patterns during sleep, each exhibiting unique characteristics.
Here's a breakdown of the different phases of your natural sleep cycle:
In the initial stage, the shift from being awake to falling asleep begins. You may feel drowsy and easily awakened. Muscle activity decreases, and your breathing and heart rate begin to slow down.
Stage 2 is characterized by a deeper state of sleep. In this stage, your brain waves decelerate, and there are intermittent bursts of rapid brain activity called sleep spindles. Your body temperature also decreases, and you become less aware of your surroundings.
Stage 3 of the natural sleep cycle is often referred to as slow-wave sleep (SWS) or delta sleep. During deep sleep, the human brain produces slow delta waves, and it becomes increasingly difficult to awaken. Deep sleep is vital for physical restoration, hormone regulation, and overall renewal.
REM sleep is where the magic happens. This is when most dreaming occurs, and brain activity resembles that of wakefulness. Despite the name, your eyes dart around rapidly under closed lids during this stage. REM sleep is crucial for cognitive function, memory consolidation, and emotional processing.
These stages of the sleep cycle go through multiple times during the night, with REM sleep periods becoming longer and more prominent as the night progresses. Each stage plays a great role in ensuring that we wake up feeling refreshed and rejuvenated.
While sleep calculators can provide valuable guidance, they are just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to achieving optimal sleep. Incorporating healthy sleep habits into your life is equally beneficial for ensuring restful nights and productive days. This includes creating a sleep-conducive environment, establishing a consistent sleep schedule, and adopting relaxation techniques to unwind before bedtime.
Let's discuss each one of these in detail:

Darkness: Ensure your bedroom is dark or dimly lit to signal to your body that it's time to sleep. If you reside in a sunny or brightly lit area, think about using blackout curtains or wearing an eye mask for better sleep.
Comfort: Invest in a comfy mattress and pillows that provide adequate support for your body. Along with that, opt for breathable bedding and regulate room temperature to avoid discomfort from overheating.
Noise Control: Minimize disruptive noises by using earplugs, white noise machines, or soundproofing materials if you live in a noisy environment.
Clutter-Free Space: Keep your bedroom tidy and free of clutter to promote a sense of calm and relaxation.

Set a Bedtime Routine: Develop a calming bedtime ritual to cue your body for relaxation. This could entail activities like reading, enjoying a warm bath, listening to soothing sleep music, or practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation.
Consistent Wake-Up Time: Strive to wake up consistently at the same time each day, including weekends, to regulate your body's internal clock. Consistency in wake-up times helps to synchronize your sleep-wake cycle and improve sleep.
Limit Napping: Avoid long naps, especially late in the day, as they can interfere with your ability to fall asleep at night. If you need to nap, keep it short (20–30 minutes) and schedule it earlier in the day.

Mindfulness Meditation: Practice mindfulness or meditation before bedtime to soothe your mind and manage stress levels. This can assist in easing racing thoughts and fostering a state of relaxation.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Engage in progressive muscle relaxation exercises to release tension from your body. Begin by tensing and subsequently releasing each muscle group, progressing from your toes to your head.
Deep Breathing Exercises: Try deep breathing exercises to reduce your heart rate and induce a state of relaxation. Concentrate on inhaling slowly through your nose and exhaling through your mouth.
Beyond what has already been discussed, there are additional valuable insights and practices to enhance your sleep health and promote better sleep hygiene.

If you're not already aware, physical activity and sleep are closely related. Consistent physical activity, especially when done earlier in the day, aids in regulating your body's internal clock and improving sleep quality. Exercise stimulates the release of hormones like endorphins, which can diminish stress and anxiety, offering a relaxed state conducive to sleep. Nonetheless, refrain from vigorous exercise near bedtime, as it may boost energy levels and hinder the ability to fall asleep easily.

Caffeine is a common stimulant found in coffee, tea, soda, chocolate, and certain medications, and impedes both falling asleep and maintaining sleep. Restricting your consumption of caffeine, particularly in the afternoon and evening, is advisable, as it may disturb your body's circadian rhythm. Consider choosing decaffeinated beverages or herbal teas as alternatives.

The blue light emitted by devices including phones, tablets, computers, and TVs can disrupt your body's production of melatonin. Aim to avoid screen time for at least an hour before you get into bed to let your brain unwind and prepare for sleep. If you must use screens close to bedtime, think about using blue light filters or wearing glasses that block blue light.

Eating heavy meals, spicy foods, or drinking large amounts of fluids before bedtime can cause discomfort and disrupt your sleep. Opt for light, easily digestible meals in the evening. Also, avoid drinking alcohol or smoking near bedtime because they can mess with your sleep. However, it's important to stay hydrated for your health, so drink enough water during the day. Just try to drink less as bedtime approaches to avoid waking up to go to the bathroom during the night.

Certain herbs and supplements, known for their calming properties, can help you relax and achieve sleep more quickly. Consider incorporating natural sleep aids such as chamomile tea, valerian root, lavender essential oil, or melatonin supplements into your bedtime routine to facilitate falling asleep fast. These natural remedies can soothe your mind and body, promoting a state of relaxation conducive to swift sleep onset.

If you've tried various strategies to improve your sleep but still struggle with insomnia, excessive daytime sleepiness, or other sleep-related issues, it may be time to seek help from a healthcare professional. A sleep specialist can evaluate your sleep patterns, identify any underlying sleep disorders (like insomnia, sleep apnea, etc.) or health conditions, and recommend appropriate treatments or interventions to improve your sleep quality and overall well-being.
Understanding the detrimental effects of sleep deprivation and recognizing the transformative power of quality sleep is the first step towards a healthier life. Sleep calculators are useful because they tell us when we should hit the hay and wake up for the best rest. By using these tools and sticking to healthy sleep habits, like having a regular bedtime routine and making our sleep space cozy, we can make our sleep better. Don't forget: getting ample quality sleep is crucial for our health and how well we get things done. So, let's make sleep a priority and reap the rewards of feeling fresh and energized each day.
The ideal time to go to sleep varies depending on factors like age, lifestyle, and personal preferences. However, most adults should aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night. If you need to wake up at 6:00 AM, for example, you might want to go to bed somewhere around 9:00 PM to ensure you get adequate rest.
Most adults require around 4-6 complete sleep cycles per night, which typically translates to 7-9 hours of sleep.
Feeling groggy after getting 8 hours of sleep can happen occasionally and is considered normal. Factors such as sleep quality, sleep environment, stress levels, and individual differences in sleep patterns can all contribute to feeling groggy upon waking, even after getting the recommended amount of sleep. If this feeling persists or occurs frequently, it may be worth examining your sleep habits and seeking advice from a healthcare professional.
As people age, their sleep patterns may change, and they may require slightly less sleep. However, even as adults, it's necessary to prioritize sufficient sleep for overall health and well-being. While some adults may function well on 7 hours of sleep, others may need closer to 9 hours to feel fully rested and alert.
While it's always better to stick to a regular sleep routine at night, occasional daytime naps can offer advantages, particularly if you've had insufficient sleep overnight or are experiencing excessive fatigue. Short power naps lasting around 20–30 minutes can enhance alertness and efficiency without compromising nighttime rest. Nevertheless, extended or irregular daytime naps may disturb your natural sleep pattern, making it challenging to fall asleep at night.
Related blog posts:
1. Sleep Apps
2. Sleep Music
4. Microsleep
5. Sleep Timer
Disclaimer: What is said in this article has been referenced from multiple sources and is intended only for educational and informational purposes. Please note that no content in this article is a substitute for professional advice from a qualified doctor or healthcare provider. Always consult an experienced doctor with any concerns you may have regarding a health condition or treatment, and never disregard any medical suggestions or delay in seeking treatment because of something you read here.
Notify me when available
We will send you a notification as soon as this product is available again.
We don't share your email with anybody


